Choking
The following information is not a substitute for a first aid course. Many organizations offer first aid training, including choking manoeuvres. Your municipality or local CLSC can provide information on courses in your area.
Your child put a candy, nut, piece of grape, or some other small object in his mouth and it got stuck there.
Your child is breathing, coughing noisily, talking, or making sounds?
Do not intervene as long as your child is still coughing noisily. This means he is trying to dislodge the item on his own. Encourage him to cough vigorously (e.g., try coughing along with him so he’ll imitate you).
Call 9-1-1 if you’re worried about your child’s breathing.
Your child is unable to breathe, cough, talk, or make sounds?

Think of the lungs as plastic bottles and whatever is blocking your child’s breathing as a stopper. The manoeuvres aim to pop the stopper off by pressing firmly on the bottles.
Illustration: Audrey Malo
- Do the manoeuvres described below and onto the next page immediately.
- Call for help and make sure someone calls 9-1-1.
Manoeuvres
Choking manoeuvres are intended to expel whatever is blocking your child’s airway. Doing so requires you to press down firmly on the lungs.
The next section shows how to do it, depending on the age of the child.
Child under age 1
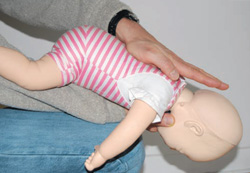
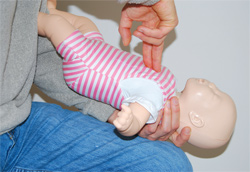
Photos: Danielle Landry
- Give 5 firm taps between the shoulder blades with the palm of your hand.
- Turn your child over and push hard 5 times with 2 fingers in the middle of their chest, just below an imaginary line between the nipples.
Alternate steps 1 and 2 until your child starts breathing, coughing, or crying.
If your child loses consciousness, see Loss of consciousness.
Child age 1 or older
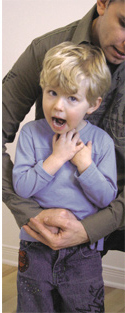
Photo: Société de sauvetage
Perform abdominal thrusts: Place your fist on your child's stomach just above the belly button, then thrust firmly inward and upward (J-shaped movement).
Repeat the thrusts until your child starts breathing, coughing, talking, or crying.
If he loses consciousness, see Loss of consciousness.
Take your child to the emergency room after a choking episode because there could be complications.


